Category: Hardware
-
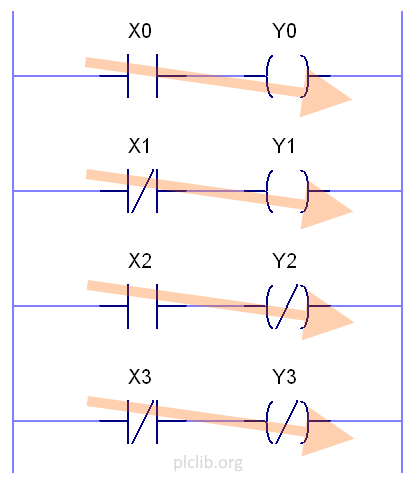
Diving into the plcLib Scan Cycle
The plcLib library implements a scan cycle which has some similarities – and also some important differences – to the traditional scan cycle of an industrial PLC. The scan cycle is defined as the repeating process of reading inputs, performing calculations and updating outputs. The scan cycle of a PLC takes place in well defined…
-
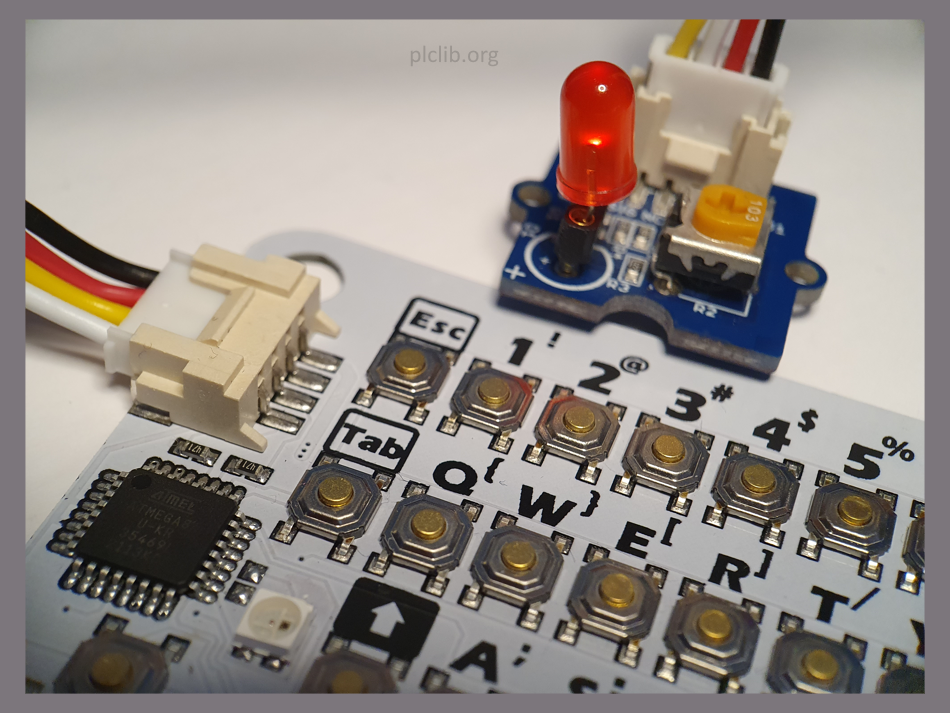
Using the M5Stack CardKB mini keyboard
The M5Stack CardKB is a full specification mini keyboard, with a built-in controller IC. It is supplied with a Grove connector and uses an I2C interface, plus the Wire library, to transfer keypress data to a connected Arduino-compatible microcontroller. Surprisingly, the entire keypad is the size of a credit card. The CardKB module offers a…
-

Using Escape Sequences to Extend plcLib
The escape sequence ‘//$’ causes the current line to be ignored by the JavaScript interpreter, but the remainder of the line is passed unaltered to the C++ compiler. Suppose for example, you need to include a servo library in your C++ application. This may be achieved by adding the line ‘//$#include <servo.h>’ at the start…
-
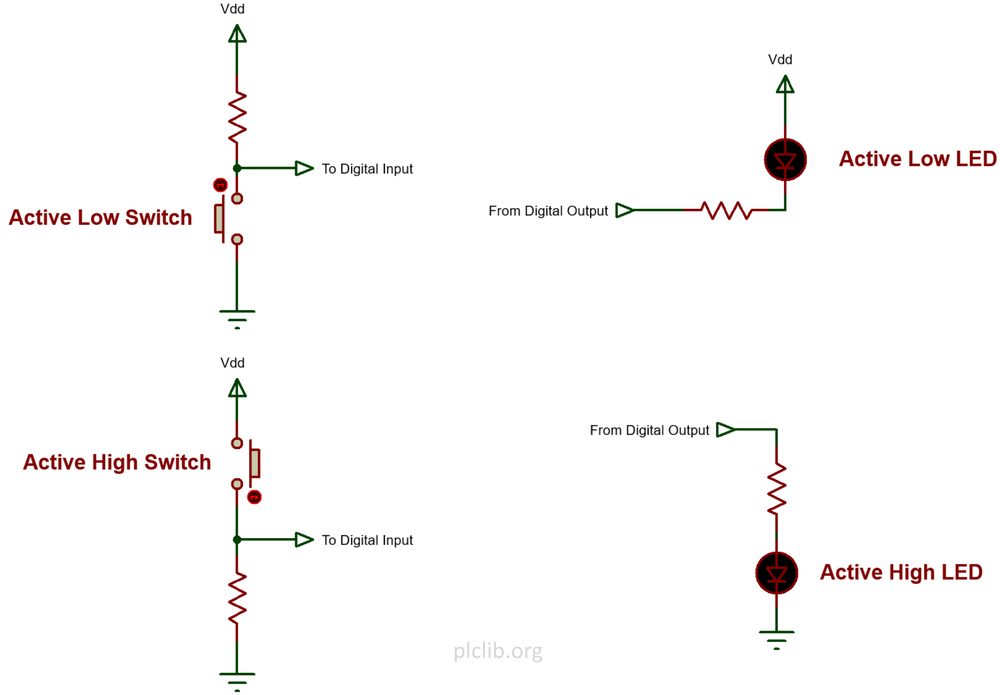
Working with Positive and Negative Logic
One of the challenges of electronics interfacing is dealing with the wide variety of electronics hardware that may be connected! Internally, a microcontroller deals with digital values that are either true or false, on or off, or 1 or 0. However, there is no single definitive mapping of internal logic values and external voltage levels.…
